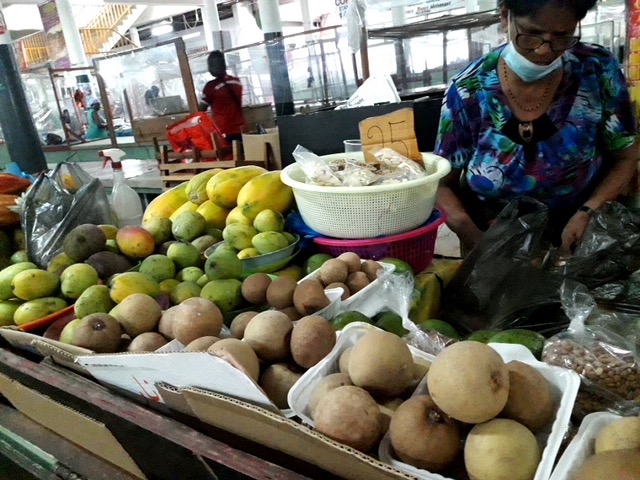
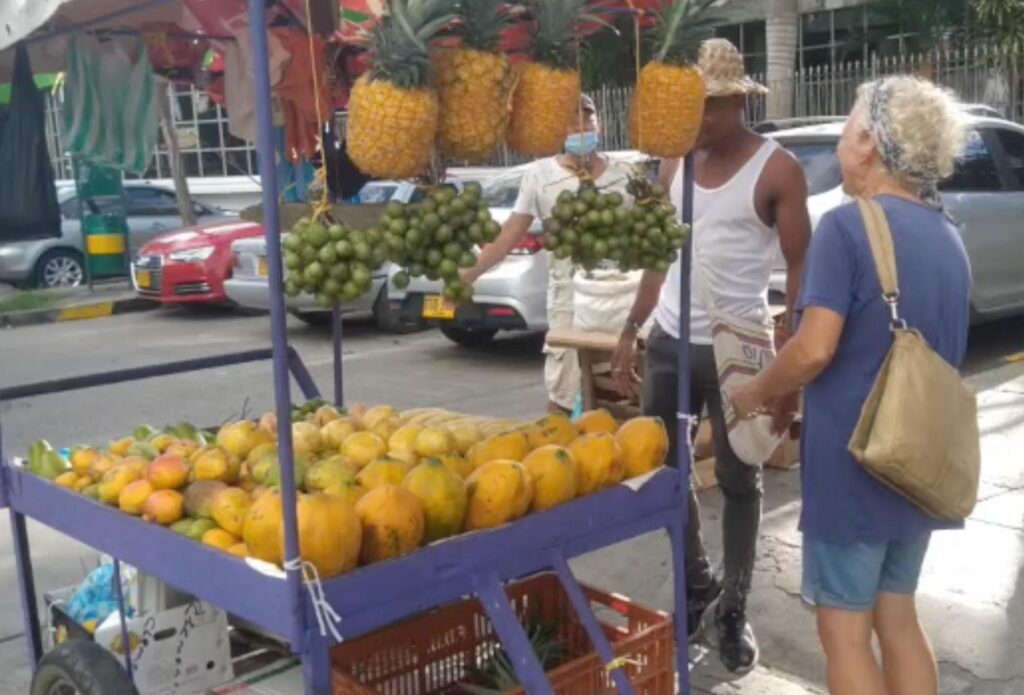
What is sweeter than sweets? When you are in the tropics, like here in Columbia, it is easy. But come to think of it, it was also easy in the Netherlands. If you don’t eat or drink sugar, fruit is the sweetest thing on earth. Especially when you eat it in the season, nearby to where you can pick it. No plastics, no chemicals. Enjoy!

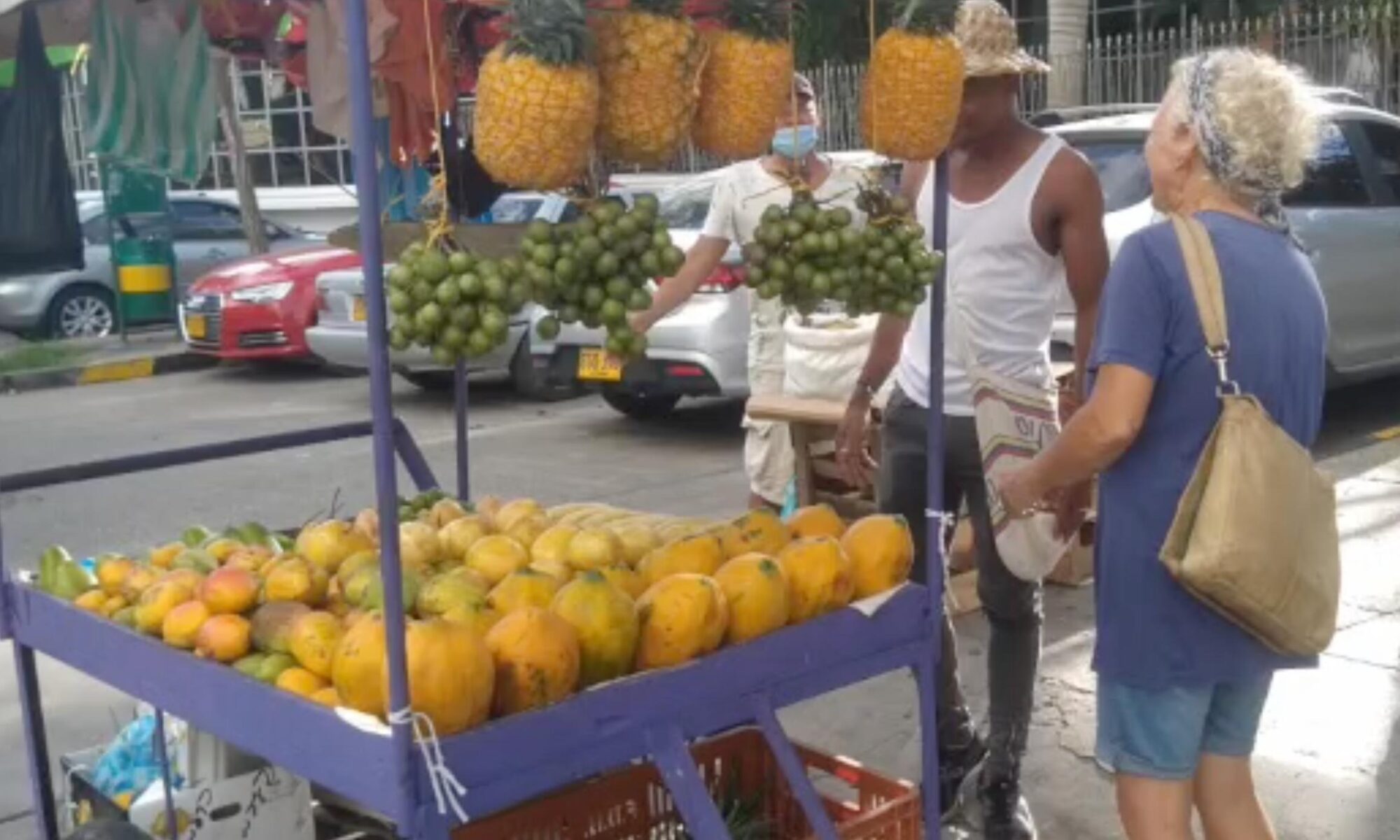
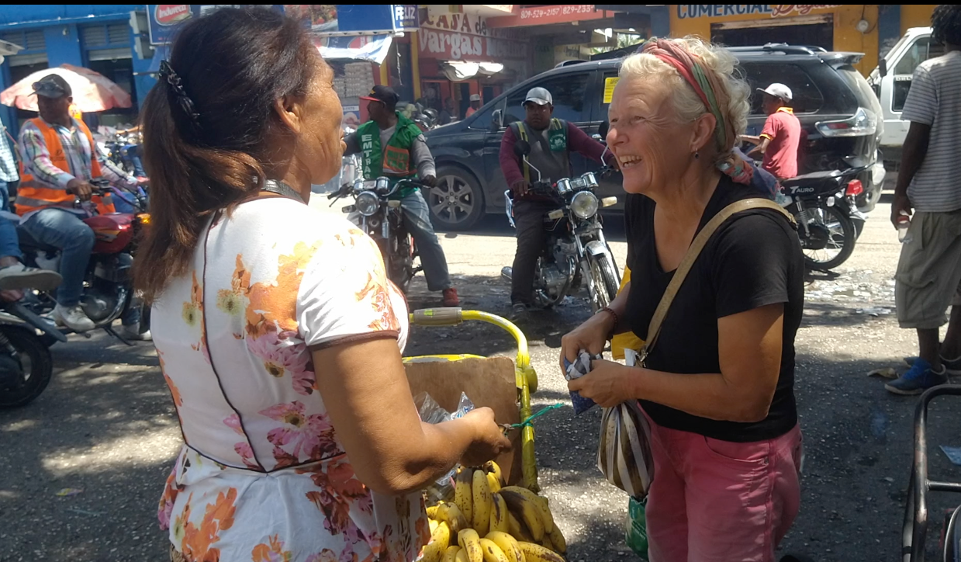
We had a young guest in Cartagena, Columbia. An amazing 8 years old girl. She wants to be an environmental scientist when she grows up, ‘just like Peter!’. And, she politely refused the ‘juice’ we had brought with us from Suriname. ‘This one is not too bad, but some drinks have only water with sugar and colorants’. She was right. And it made us think.
When we are working on our computers it is easy to eat sweets, like these:
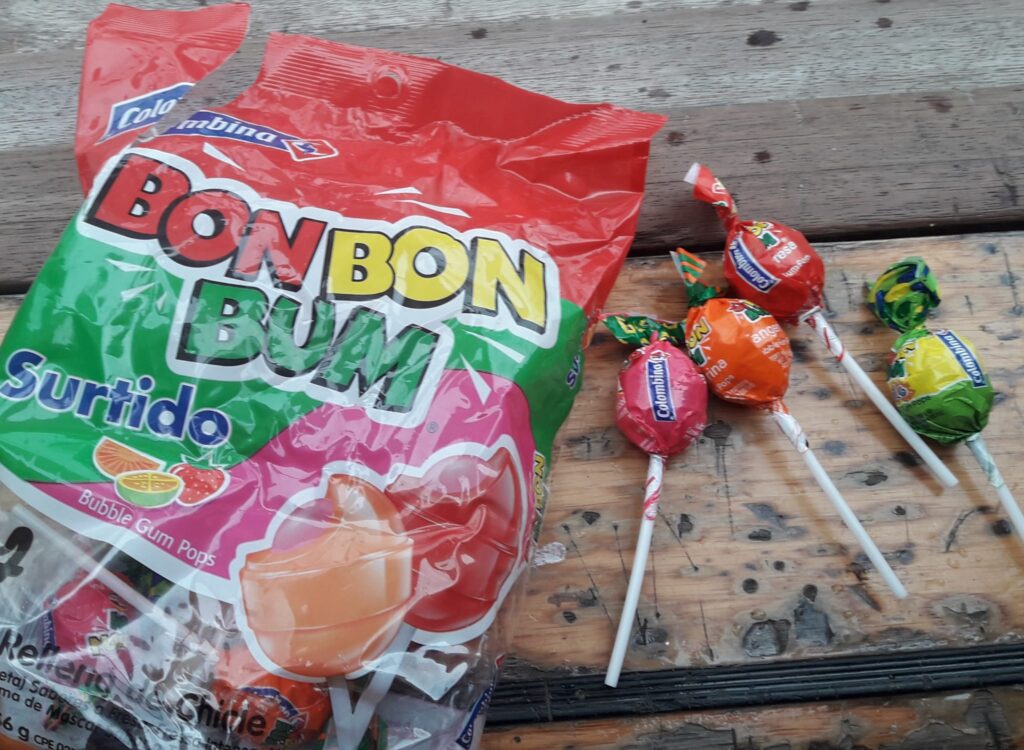

We will enjoy these artificial sweets as a ‘guilty pleasure’ and dispose of the plastic responsibly. But, we certainly will eat less of them, especially now we are in Columbia where you can buy incredible fruit from the street vendors!
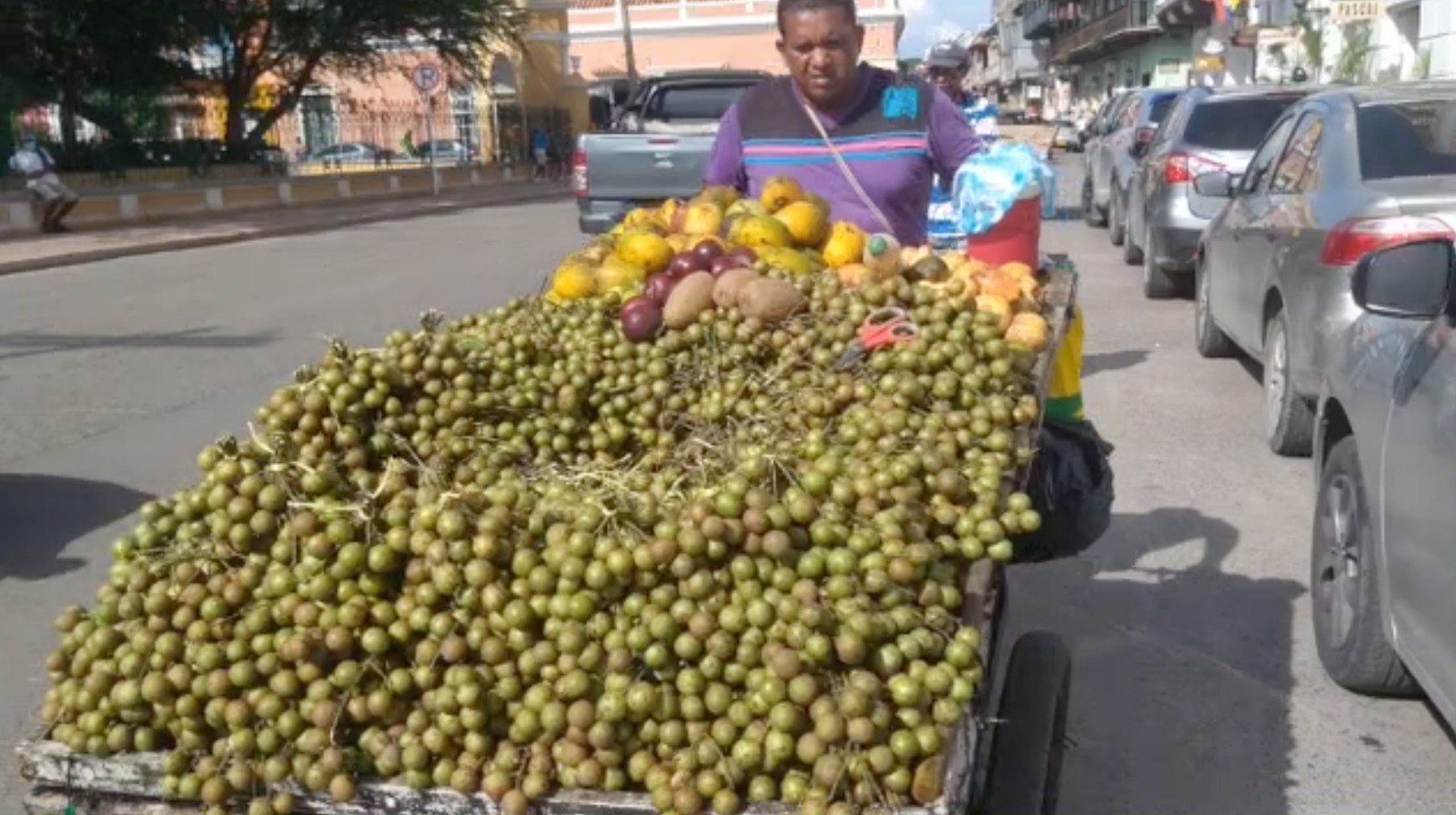
A selection:
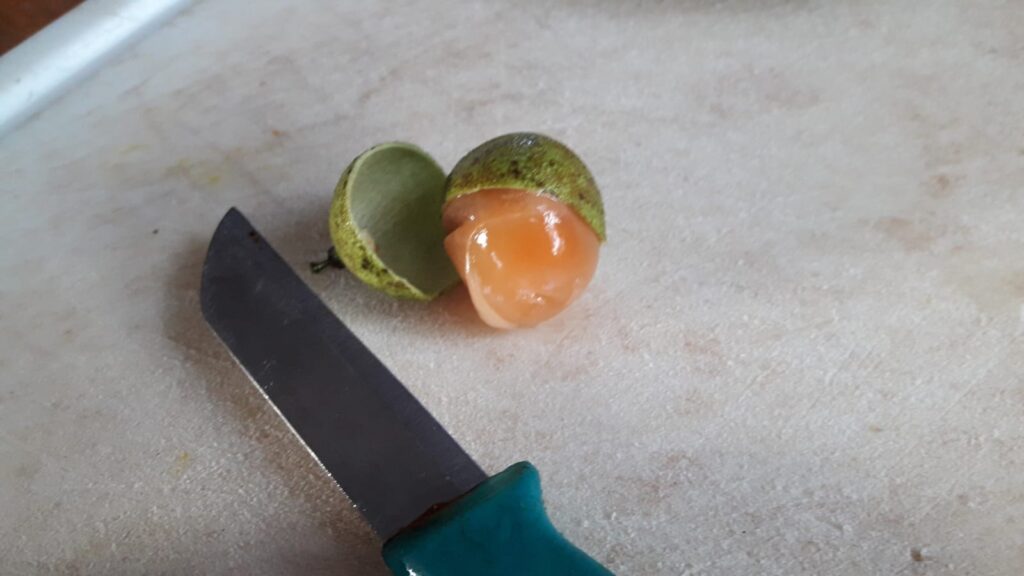

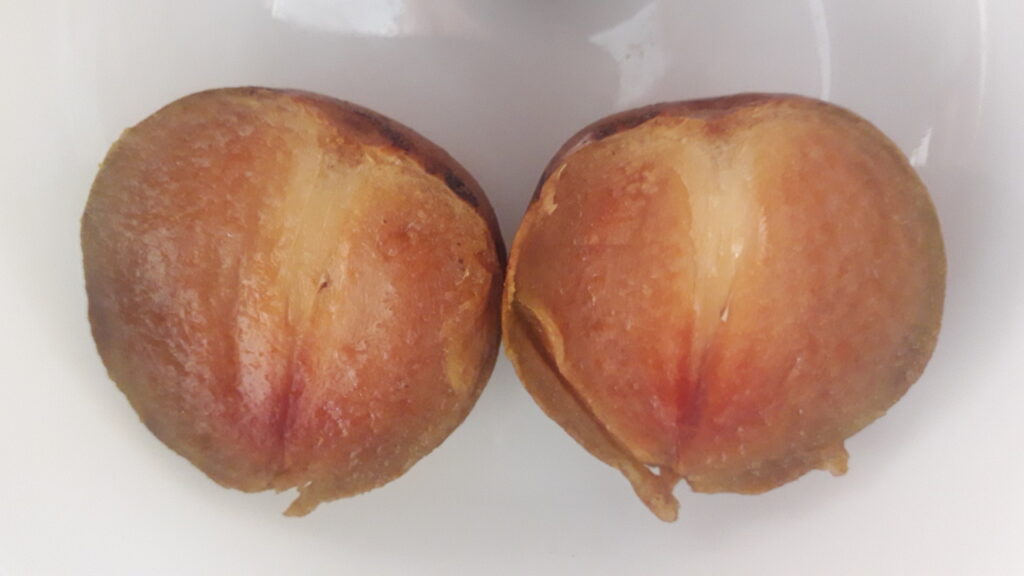
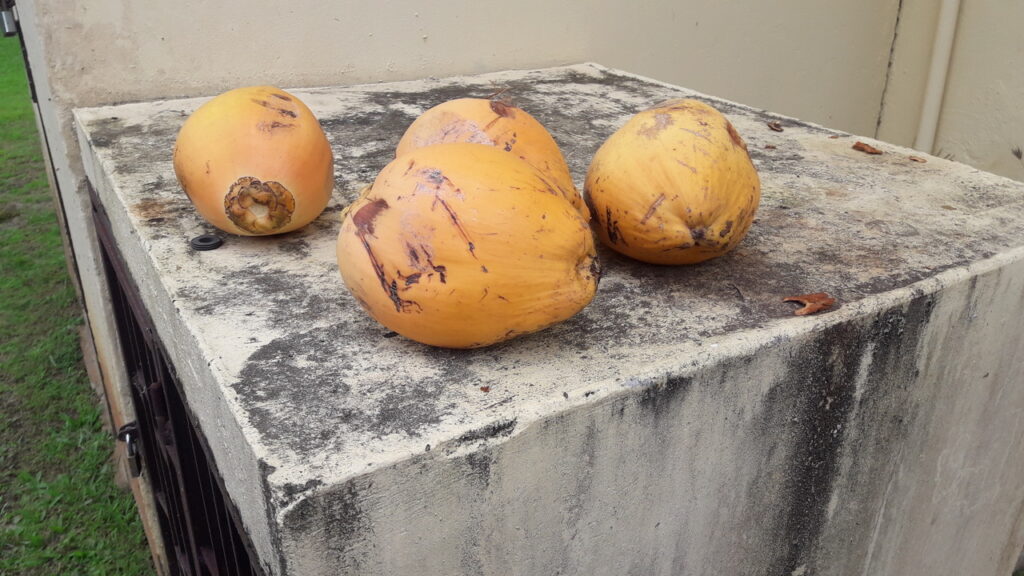
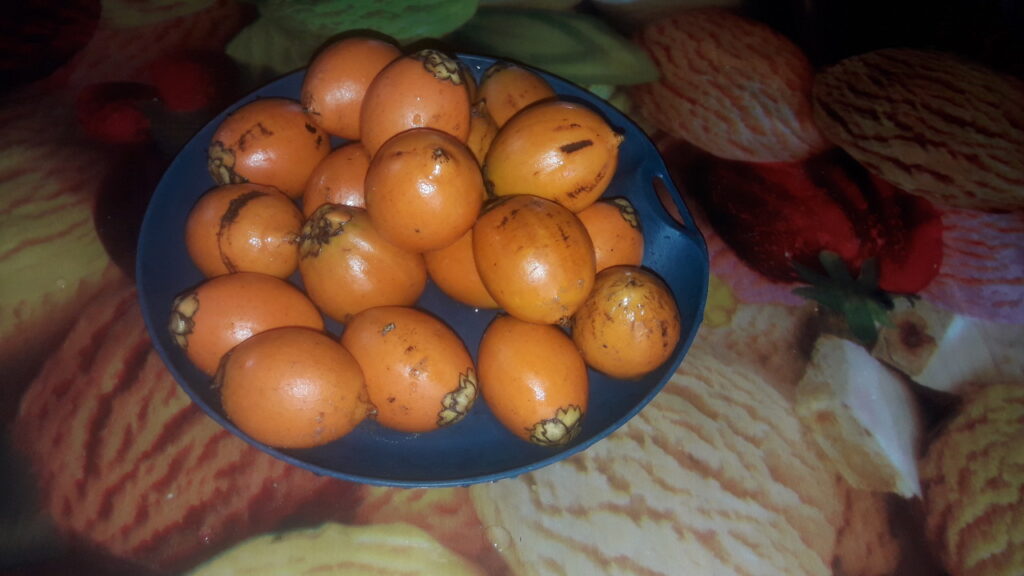
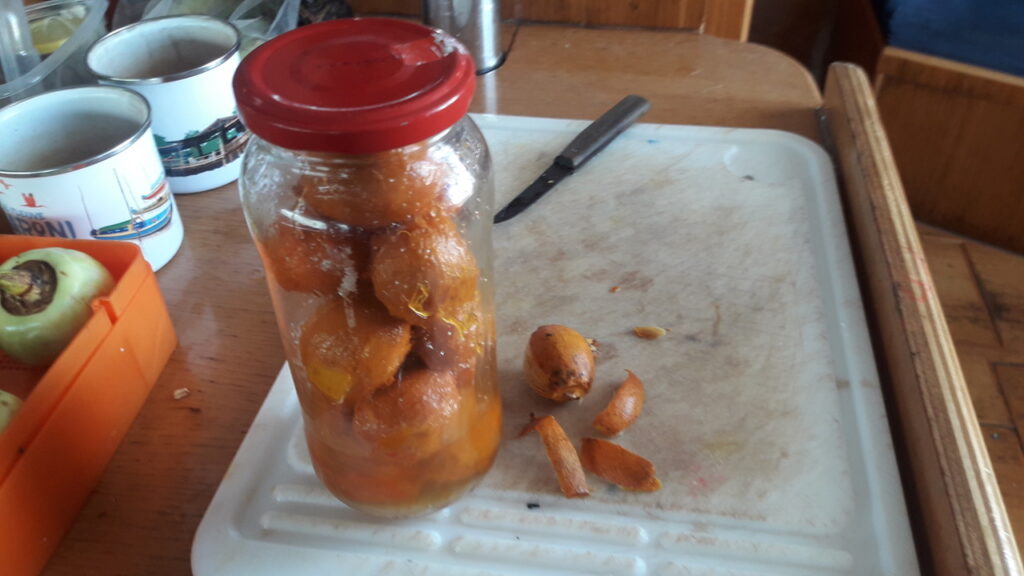
A little gem. You can slice the peel of or just crack the shell with your teeth and suck out what is inside. That may take a while but it is sweet and a little acid closer to the pit. When you feel like binge eating, it is a great alternative for peanuts.
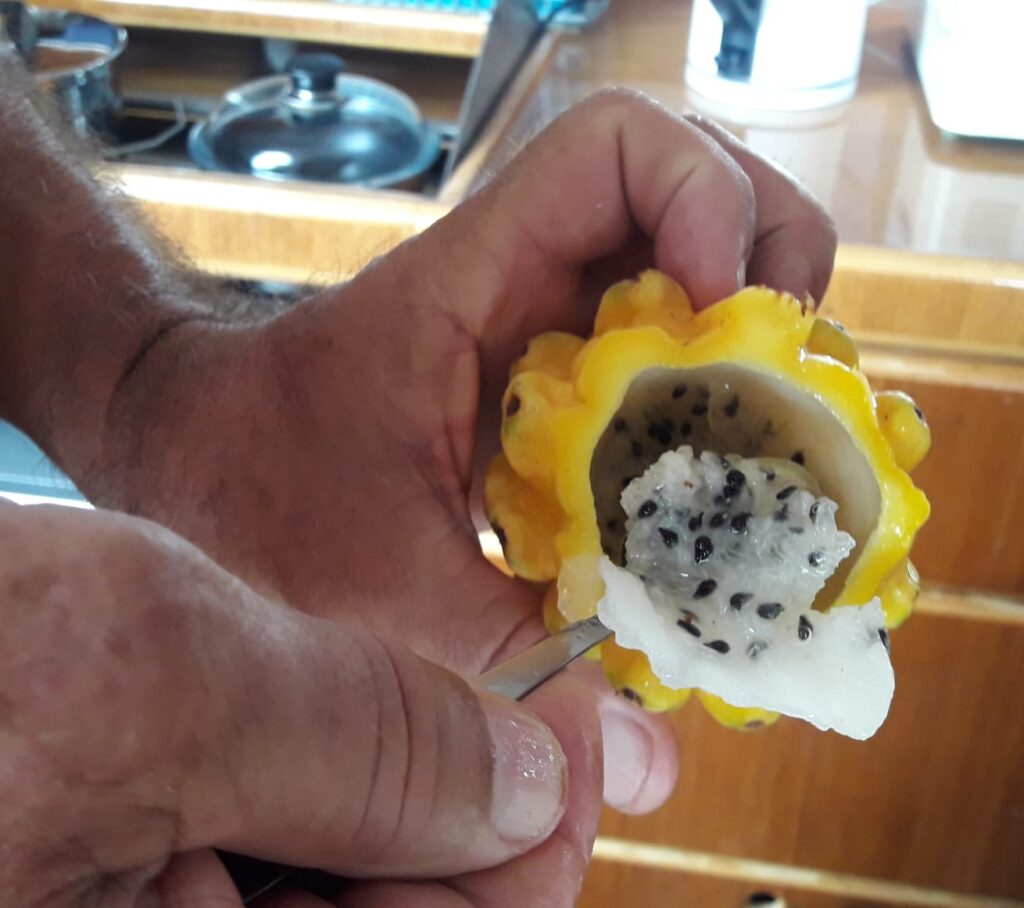

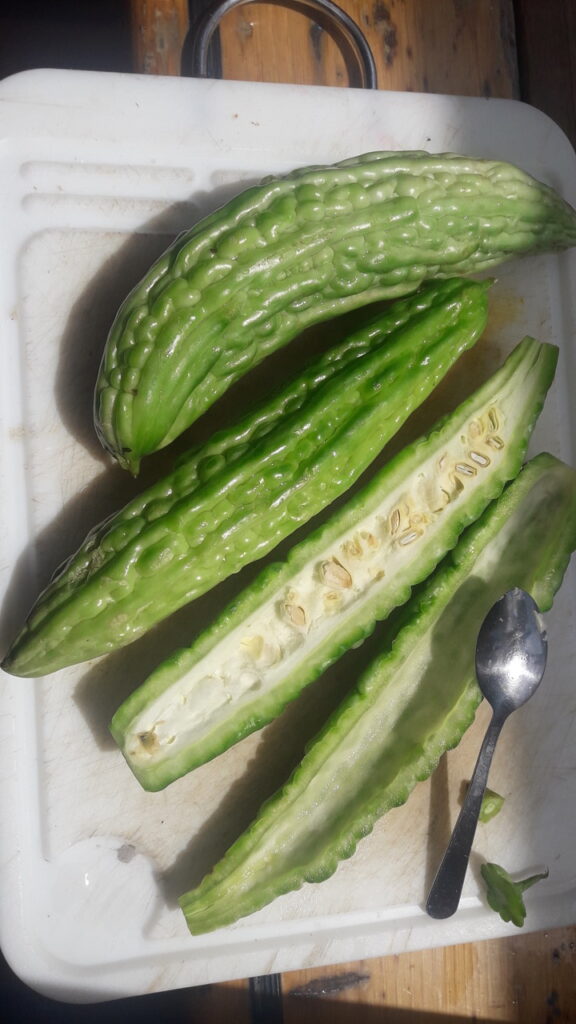
This exotic fruit is believed to originally come from Colombia. The pitahaya generally has yellow or red skin with white flesh and black seeds. You can only eat the inside.
Chop of the head and you easily spoon the inside out in one move. It tastes nice, refreshing and sweet. The seeds are not hard but crunchy.
As beautiful as it is, it’s not known to be a love potion, but it is supposed to be good for your bowels.
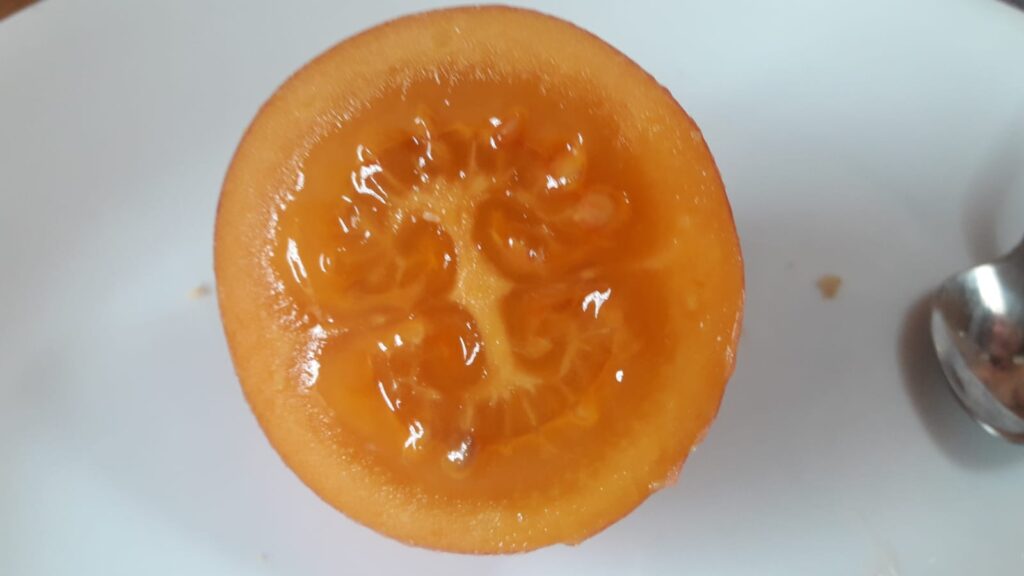

This fruit has a smooth skin that is orange and red when ripe. You cut it in half. You can eat it out with a spoon, or just take a bite out, mold it a bit, take a bite again, till you hit the skin. The intense orange pulp is fleshy. It tastes a bit like a tomato and is rich in vitamins A, C and E as well as iron, potassium and magnesium.
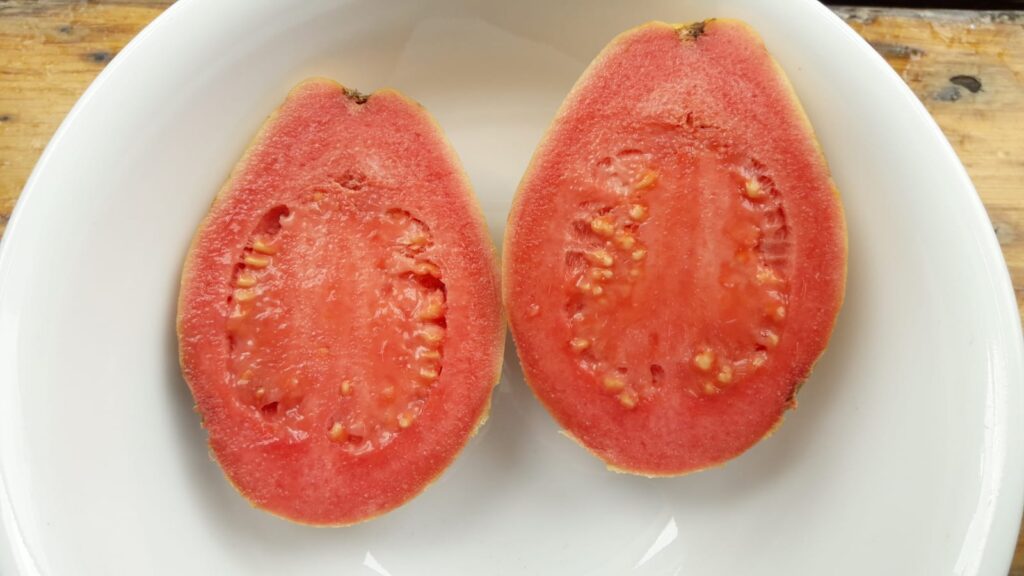

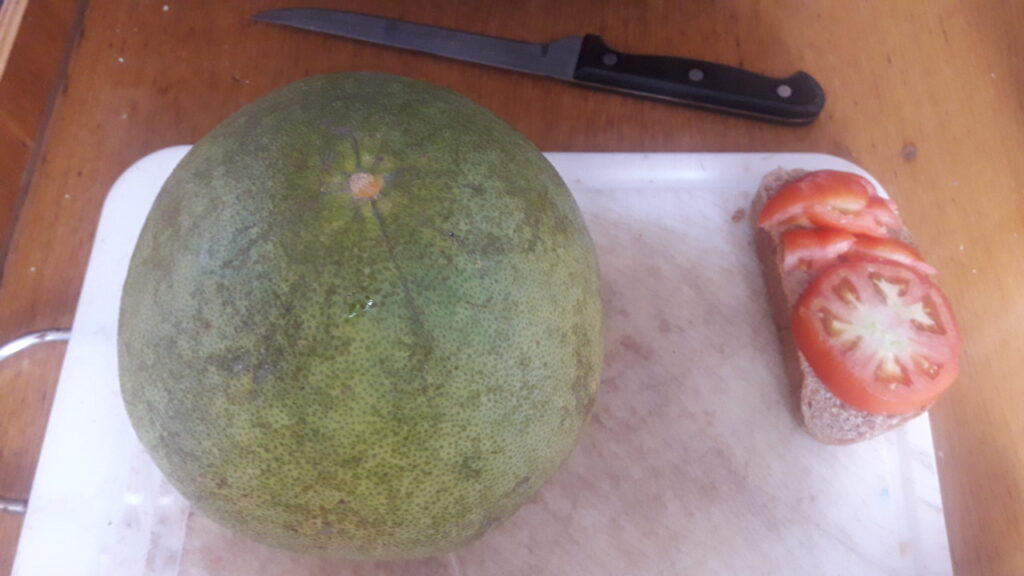
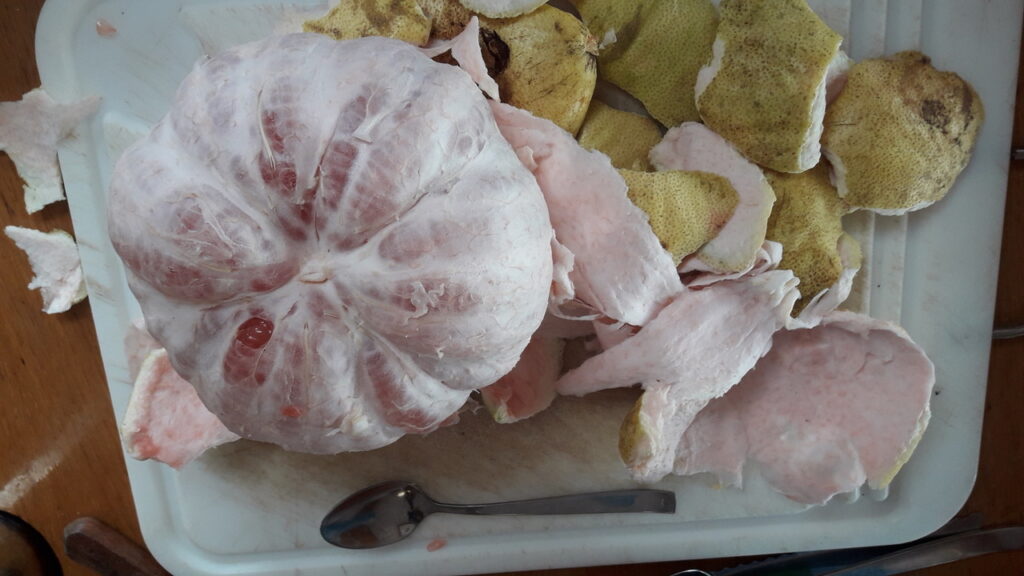
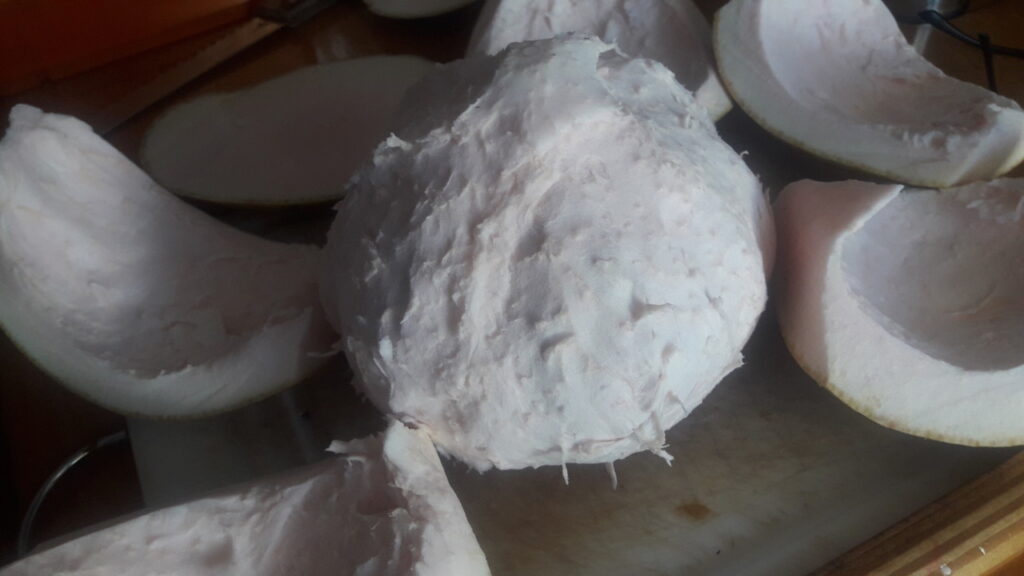
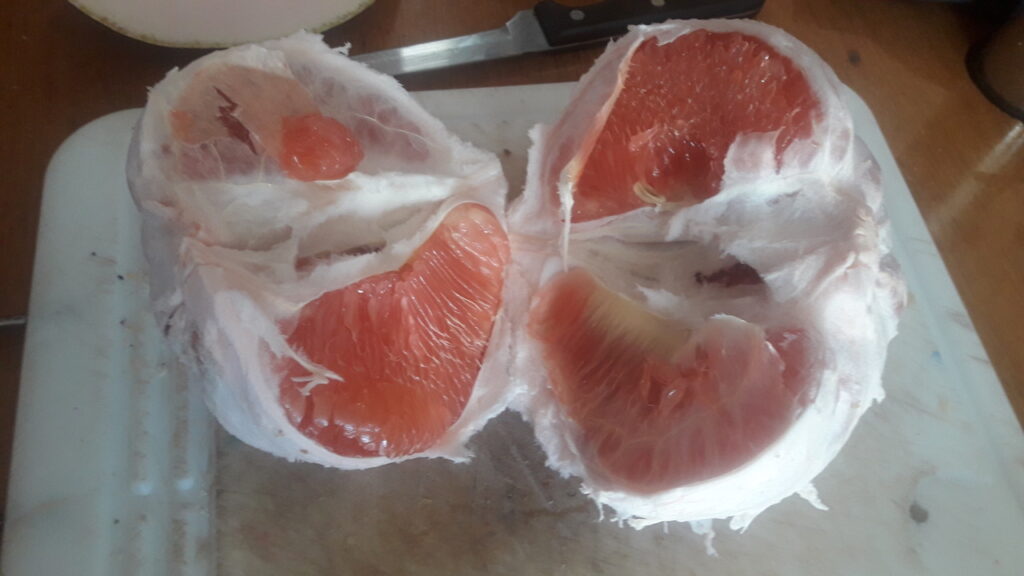
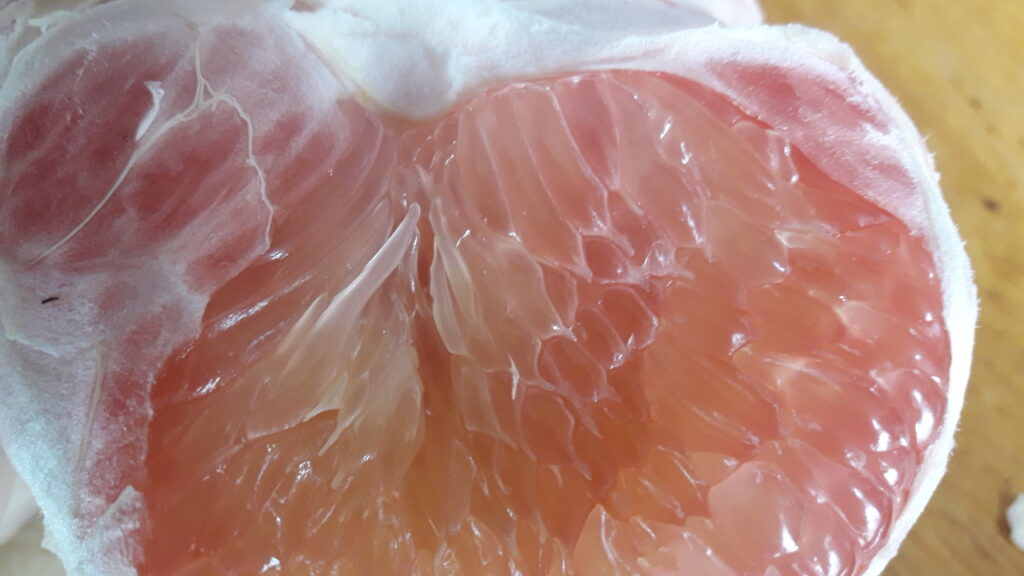
Guava is used for the most exquisite pink drinks. You can also eat them; peel and slice or spoon it out. They also make all kinds of jams and jellies, but then the colour turns into a slightly dull brownish orange.
The flavor of guava is complex and rich. Despite the hard seeds, it is definitely worth a try. It is fruity, but it is not very sweet. But you can also taste hints of flowers and spices.
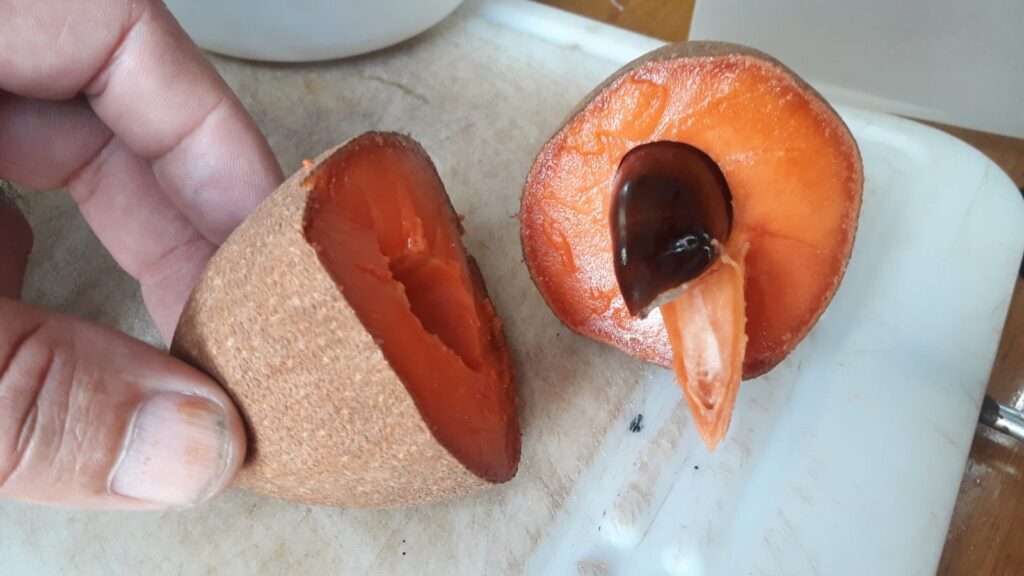

The sweetest fruit we met so far. It looks a bit like a kiwi, but bigger. We cut it in half around and were surprised to find a big pit. Take it out. Mamey has a custardy texture with a flavor reminiscent of sweet potato, mango, and papaya.
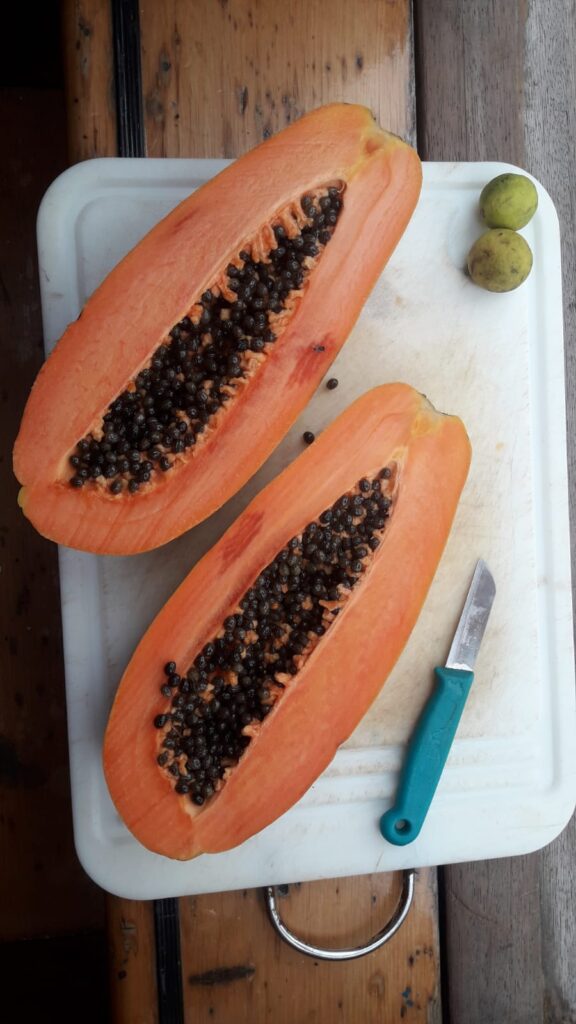

You can find Papaya anywhere in Middle-America. It is well known for its specific taste and a good source of vitamin A and C. You cut it over the length and take the seeds out. The taste of this fruit is very specific and kind of heavy. When you also eat a coincidental seed, there is a pepperish addition to it.
We like to eat Papaya with something else, like with some yoghurt and muesli in the morning. The combination with lime adds freshness.
They don’t keep really well. So, if you get a big one (which is not uncommon here) you can easily make lots of jam or ‘dulce‘.
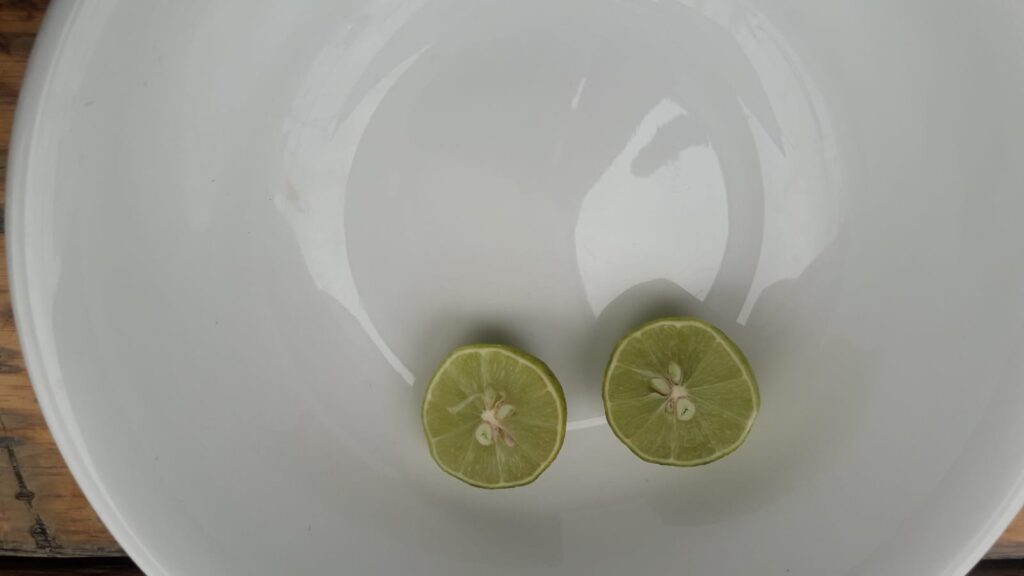

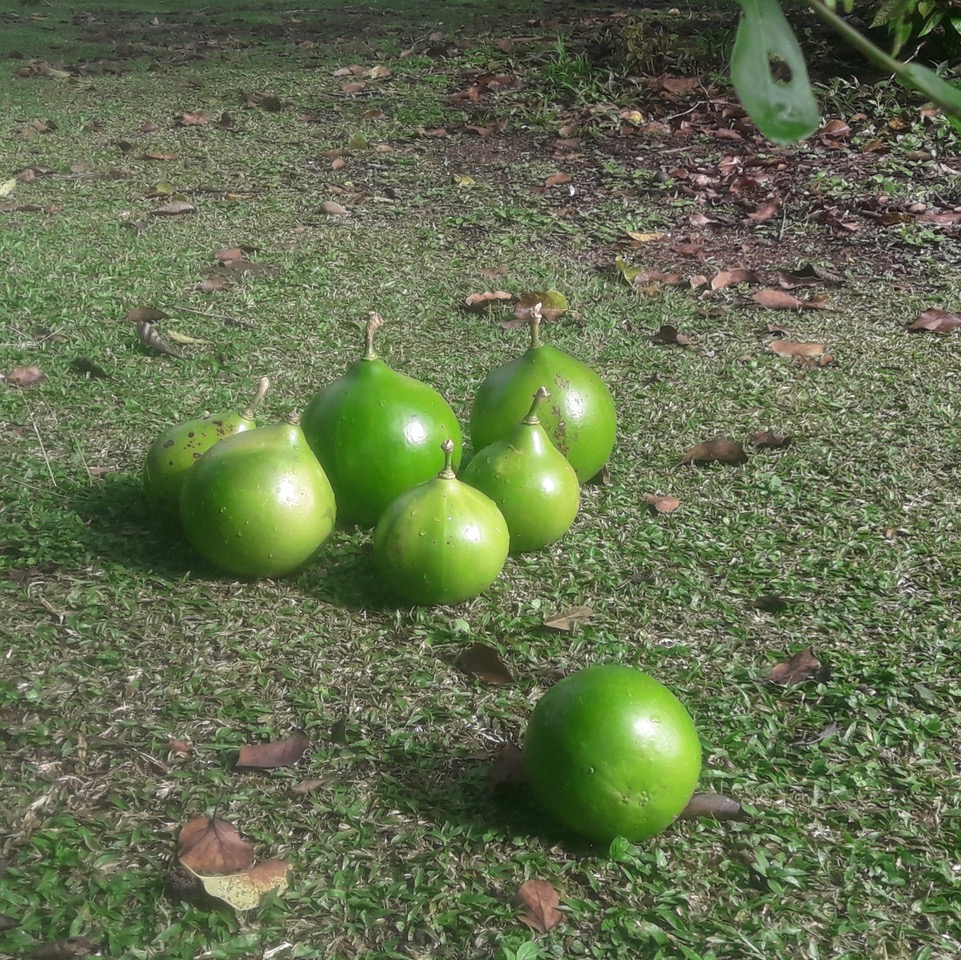
Lime is indispensable. You can buy them everywhere, in large quantities, and cheap. They keep long if they’re not in the sun. Even if they turn yellow or brown on the outside, they are still fresh and green when you slice them open. They are served with every dish. Rich in vitamin C and less sour than lemons, they have become our favorite addition to afternoon tea.
So, you can imagine that this sweeter than sweet fruit has drastically reduced our bad taste for artificial flavours and plastic wrapped ‘sweets’.
Want to know more?
Comments? Sail with us? Please contact us on: info@fossilfreearoundtheworld.org