Sustainable development is -very short- that development for a generation to make its living in such way that it doesnot compromise the future of next generations. That means clean air, water, soil, the environment. But, one can also compromise another with risks. Risks according to that clean air, water and soil.
A risk consist of two factors: the chance of an occurence and the size of that occurrence.
Two examples. The risk on a terrorist attack killing 10 people in Rotterdam during this year, would be a big occurence. But still the risk is low, as the chance is extremely small. But-next example- the risk that 10 people will be killed in that same year in Rotterdam by traffic, is way bigger. This is because the chances are big, by its frequency. Evidence: It happens nearly every year in Rotterdam.
By the way, the risk on being killed by a terrorist attack, feels much bigger -it is scary! But in this article the risk is treated without emotions, to keep it rational and debatable.
Politicians and sustainable development
Sustainable development means in short: That development that doesnot compromise the development of future generations. Nearly all countries of the world have agreed on that.
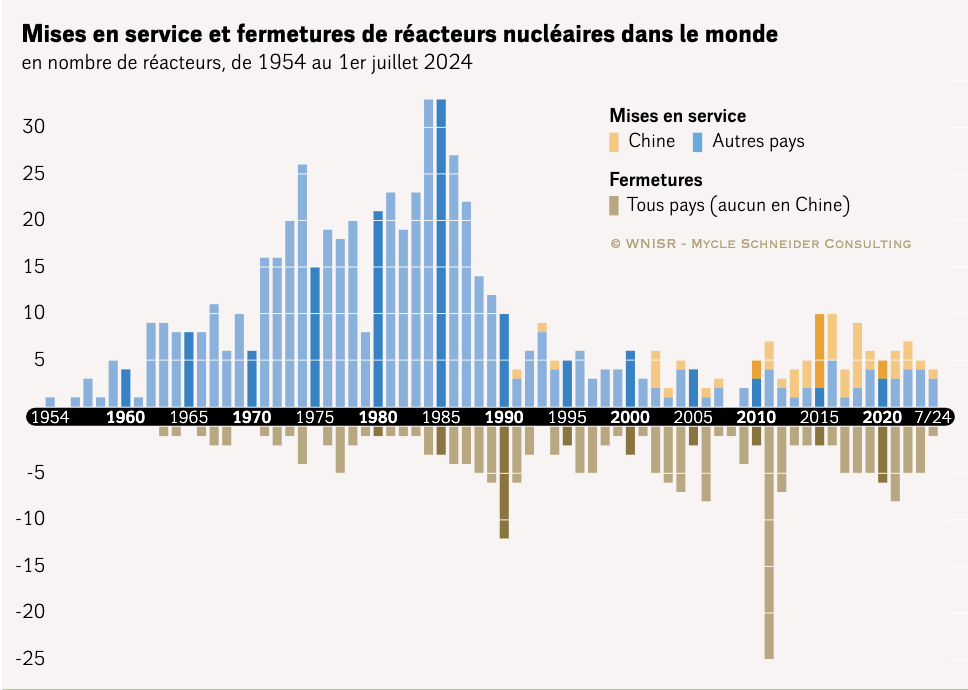
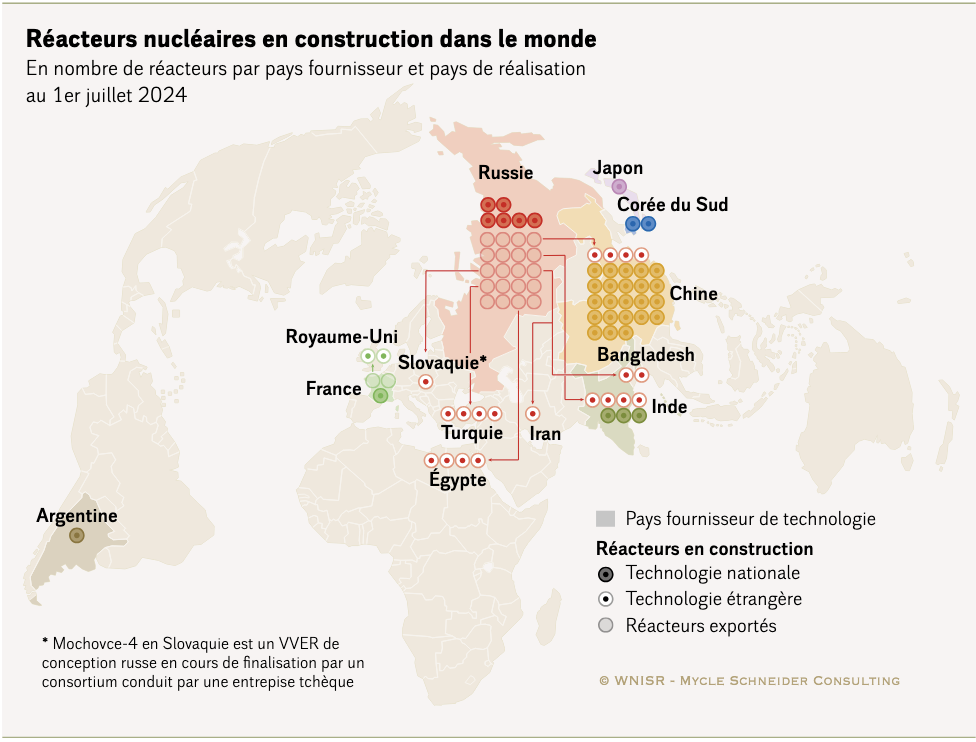
Since the French government managed to get the European Union to decide that nuclear energy would be ‘sustainable energy’ in Europe, more politicians take the liberty to promote nuclear energy as the best alternative to fossils. There are even politicians going for the construction of new reactors, before they know risks on disasters and the risks on nuclear waste. And, the radioactivity of it breaks down slower than most of our decision makers seem to comprehend. See the picture below; the risk impact counts for many many generations.
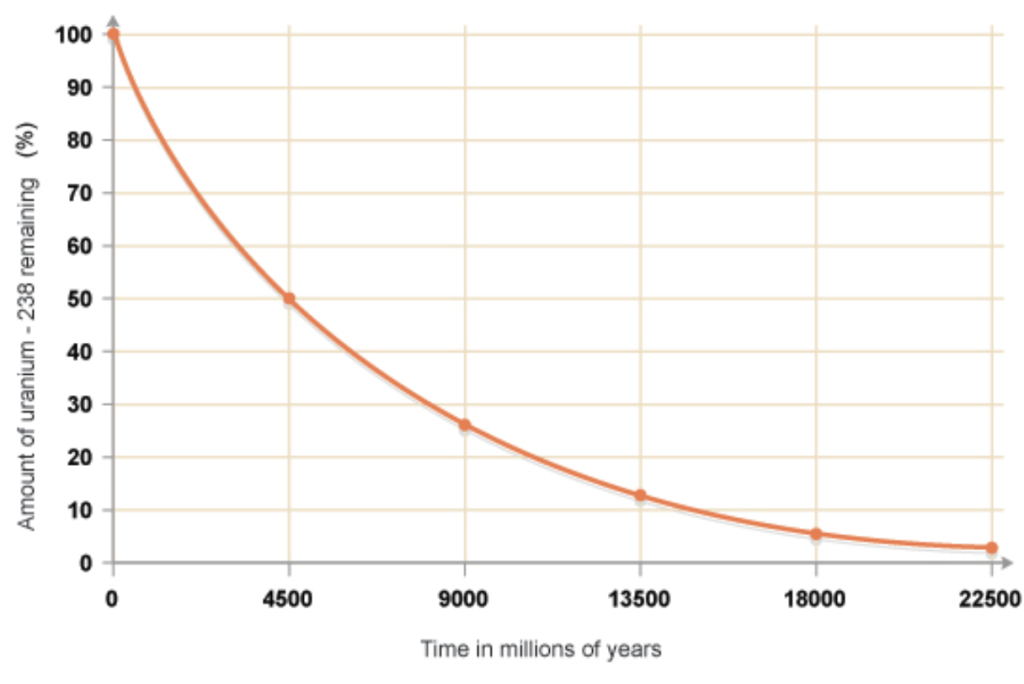
Would our decision makers not know all this – or they don’t care at all?
It looks like the latter, because they never checked the alternatives with a short half time. I could find one little exception. In 2020 the Dutch government wrote a letter to the Dutch Parliament that a research will be done on Thorium as an alternative to Uranium. The nuclear radiation of the waste could possibly be thousands of years shorter and the waste would be way better recycable. (by the way, the Wiki page on Thorium doesnot mention these facts). And, Thorium is abundant everywhere in the world, whilst Uranium is rare and ‘big business’.
Meanwhile, the decision makers go for the Uranium/Plutonium.
We have to accept that in countries like France, the UK, Spain, Slovakia and the Netherlands, the majority of the decision makers think and act according to the new defined European ‘sustainability’ and they have left the original sustainability as defined and agreed upon in 1988.
This means that they decided, not to take the risks into account that can be experienced by the next some thousand generations have to live with the risk we leave behind.
Finlands integrated waste treatment
The construction costs of a nuclear power plant are always higher than planned. Now, Finland is the first country that also set the requirement to include the waste treatment in a sustainable way. Geologically, Finland has the luck that the earth crest is really calm, and without any earthquakes. They are able to bury the waste. They managed to create a system till half a kilometer underground, and then cover the nuclear waste with clay layers and concrete plugs.
Finland managed to develop a nuclear waste system that would be sustainable. It is a system to deepbury it, half a kilometer under ground, in a geologically called ‘calm’ earth crest.
The difference between the quoted and the real costs was extreme, and never published. But, to give an idea: The Finnish construction was schemed on one decade, but it has cost an extra decade to do all the unforeseen work.
The nuclear waste appears not to be stored safe
Even nowadays, not every country acts like Finland. In 2024 the Dutch government decided to go for the construction of at least one nuclear power plant. Without any sustainable solution for the nuclear waste. And, in this same year, there have been dozens of attacks on Dutch infra structure, varying from large cyber attacks to concrete destructions on our energy infra structure, such as cables on the seabottom. https://www.rijksoverheid.nl/documenten/jaarverslagen/2025/04/22/mivd-openbaar-jaarverslag-2024
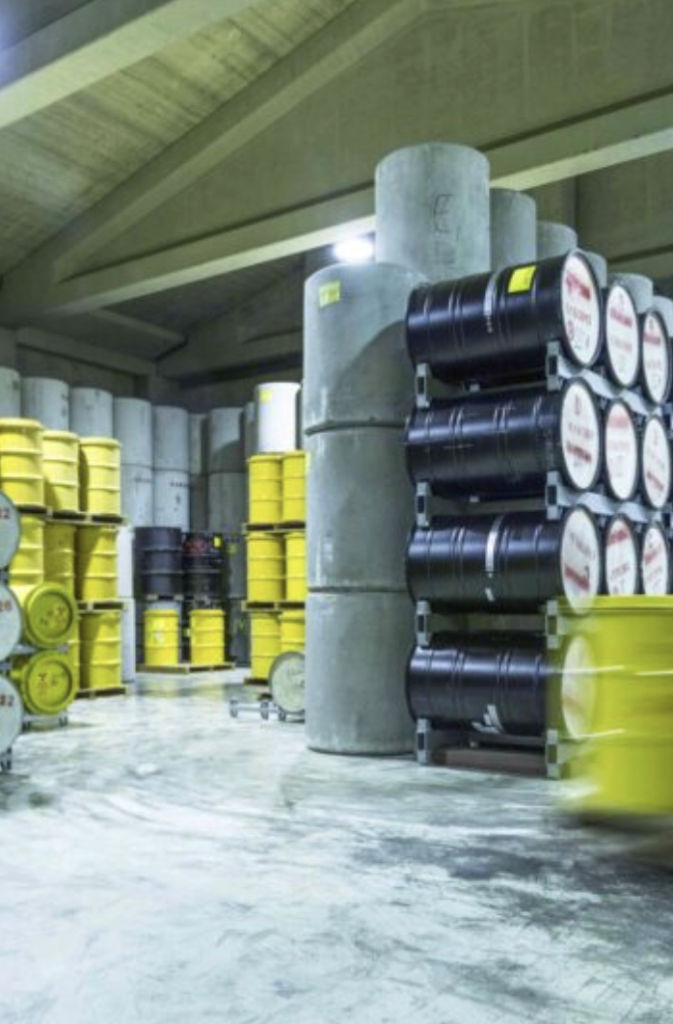

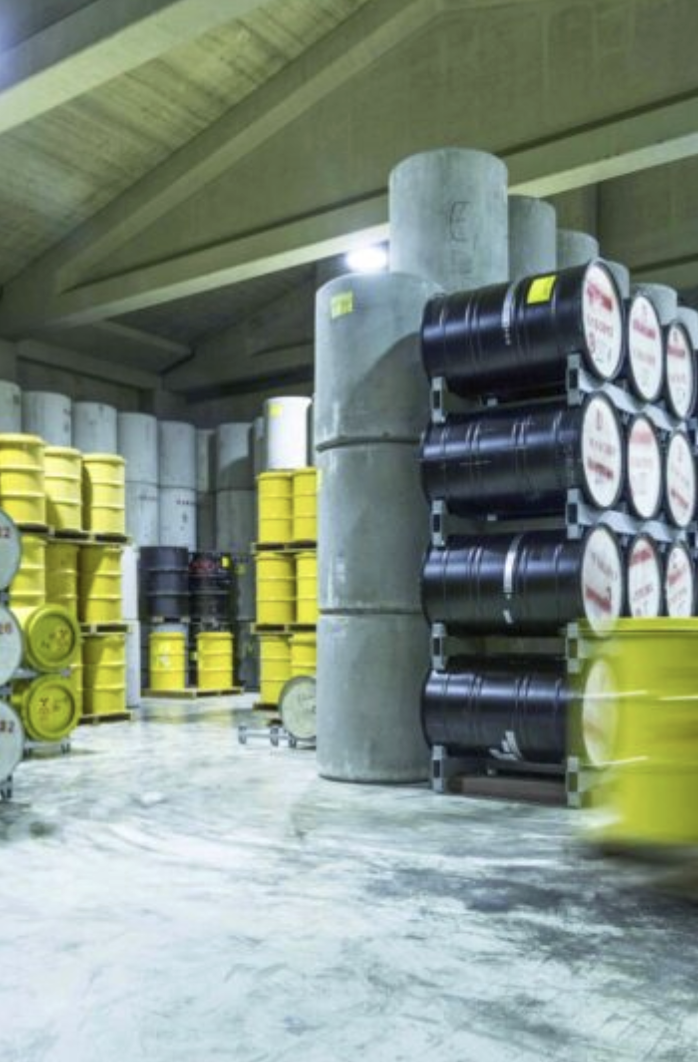
The words of COVRA on its website: “All radioactive waste is safely stored by COVRA for at least one hundred years in specially designed buildings. The waste is isolated in a central location where it can be controlled and monitored, so that safety is guaranteed over that long period.
There is no further explanation about the word ‘guaranteed’. A package of (most probably) lead and concrete, garantees no leaks for one hundred years for sure, if one keeps it here. But an attack with explosives would ask for a much much stronger protection, like some meters of material.
The text continues: Ultimately, the waste must be placed in a final storage facility. This ensures that the waste will still be outside the human habitat for thousands of years.”
The “final storage facility” is not there yet. I could perhaps be somewhere in salt mines, but it still has to be found, found out, and decided.
Only the design and construction for such a storage has cost Finland many millions more than was foreseen.
It seems a nuance, but the “thousands of years” could better be replaced for “many thousands of years”, just to be aware of the length of time. A geological time. This storage requires to be free of earthquakes and other moves of the earth crest.
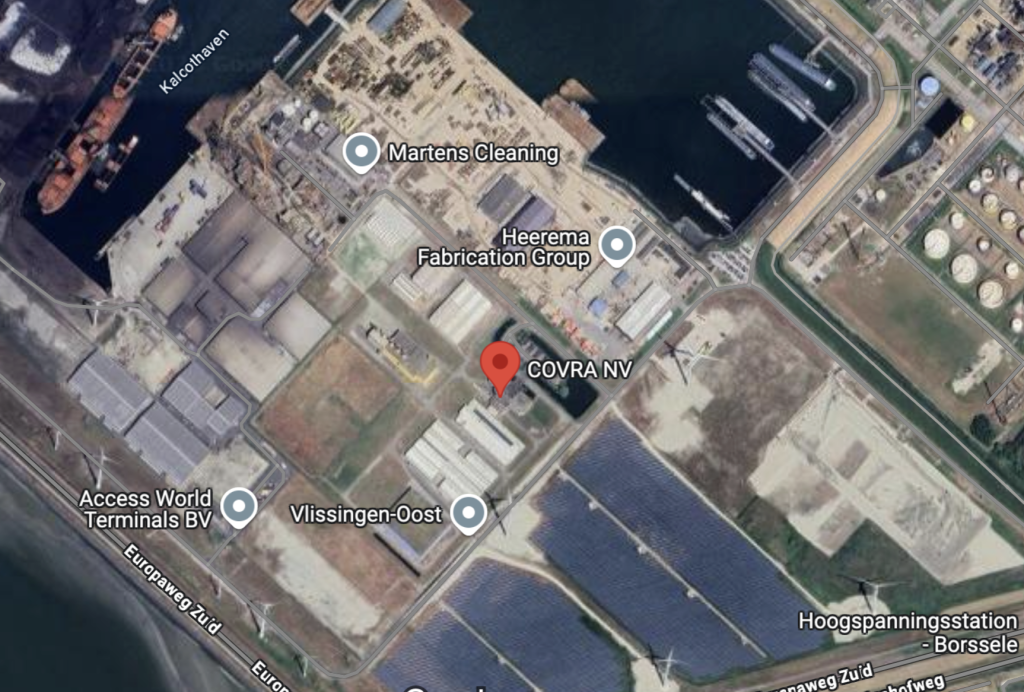
The COVRA writes on its website that all the nuclear waste is centrally managed on one place. COVRA even includes the address, on the website and in Google Maps (includes the coordinates). So easy does it, the enemy only needs one missile.
It is situated in South West Holland. With the prevailing South Western winds, the fallout will cover the people, soil, builings, everything, of half the Netherlands. And the wind doesnot stop at the German border. In the following years the illnesses and deaths will rise.
That is not safe, not even for the current generation of people.
Conclusion on the waste risks
The treatment of nuclear waste, is often not integrated nor worked out to the very detail, and never worked out with a sustainable risk for the next thousands of generations. Finland is the exception, where the waste treatment is integrated. That has doubled the planning time and the costs. But, Finland is the exception.
If we put the nuclear waste treatment in the Netherlands as an example:
- It is not sustainable at all; the risks are for the many thousands of generations after us.
- It is unsafe already for the current generation, since Russia attacks Europe on its infra structure.
The problem is not the COVRA. This company only is the symptom.
The problem is that our decision makers seem to run away with an idea, convert that to a plan for construction. But it lacks the necessary sustainability, the common sense one mostly learns from the parents and friends.
It is reasonable to conclude that our decision makers don’t act with this common sense. .
Best is to prevent that our decision makers can deal with risks and great dangers anyway. The best and only option is to power your energy needs from renewables-with-battery in your household. Most probably it is also cheaper.
In the next article the focus will on the cause of our… eh.. disinformation? Naivety? Neglectance?